Popular
How to Build the Perfect Oral Care Routine in 2025
Jul 30
Why Your Gums Bleed and How to Fix It Fast in 2025
Jul 30
Top 5 Oral Care Mistakes and How BrushO Fixes Them
Jul 29
What Makes a Toothbrush “Smart”?
Jul 22
BrushO Smart Toothbrush: Gentle, Powerful, Travel-Friendly
Jul 19
BrushO: The Future of Smart Oral Care—Redefining the Way You Brush
Jul 17
Back
How Tooth Loss Changes Bone Structure in Your Face11h ago
11h ago
Tooth loss is often viewed as a localized dental issue, but its effects extend far beyond the mouth. Each tooth plays a vital role in maintaining jawbone density, facial symmetry, and structural support for soft tissue. When teeth are lost, the surrounding bone gradually resorbs due to reduced stimulation, altering facial contours and accelerating visible aging. Understanding the biological mechanisms behind bone remodeling after tooth loss highlights the importance of preventive oral care, early intervention, and advanced monitoring technologies that support long-term structural health.
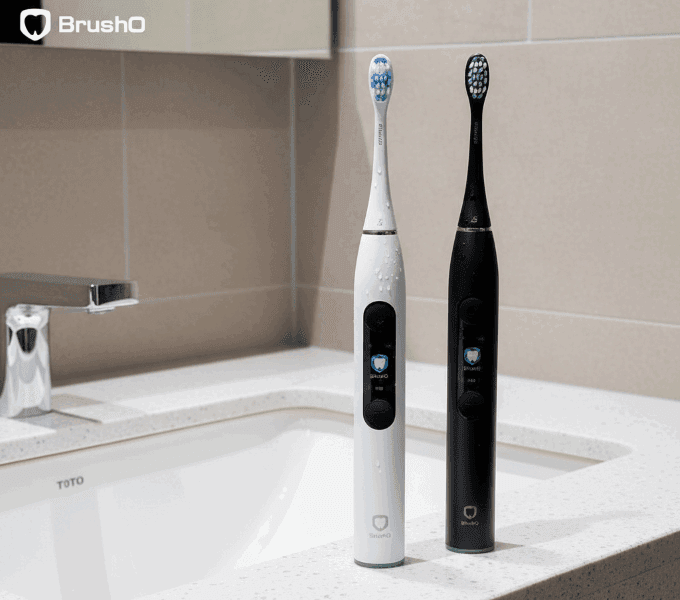

Why Teeth Matter for Bone Health
Teeth are not just functional tools for chewing — they are biomechanical stimulators of the jawbone. Every bite and chewing motion transfers force through the tooth root into the surrounding bone tissue. This mechanical stimulation signals the body to maintain bone density through continuous remodeling.
Healthy teeth help preserve:
• Jawbone volume
• Facial symmetry
• Muscle attachment stability
• Soft tissue support
Without this stimulation, bone maintenance mechanisms slow down.
The Biological Process After Tooth Loss
Bone Resorption Begins
When a tooth is lost, the alveolar bone that once supported it no longer receives mechanical stimulation. The body interprets this as unnecessary tissue and gradually reabsorbs it. This process can start within months and continue for years.
Consequences include:
• Reduced bone thickness
• Decreased bone height
• Altered jaw structure
Bone loss is permanent without medical intervention.
Changes in Facial Structure
As bone volume decreases, external facial changes may appear:
• Sunken cheeks
• Thinner lips
• Shortened lower face height
• Wrinkling around the mouth
• Reduced chin projection
These changes contribute to premature facial aging and altered expression dynamics.
Bite and Alignment Instability
Tooth loss affects neighboring teeth and bite mechanics:
• Adjacent teeth may shift
• Opposing teeth may over-erupt
• Chewing force distribution becomes uneven
This further accelerates structural imbalance and joint strain.
Long-Term Functional Impacts
Beyond aesthetics, bone changes influence:
• Speech articulation
• Chewing efficiency
• Digestive effectiveness
• Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) stability
Maintaining dental integrity is therefore a whole-system health priority.
Prevention: Protecting Bone Through Oral Care
Plaque and Gum Disease Management
Periodontal disease is a major contributor to tooth loss. Controlling bacterial buildup helps preserve supporting structures.
Proper Brushing Pressure and Coverage
Aggressive brushing or missed zones increases gum and bone risk.
Routine Monitoring
Early detection of inflammation prevents progression to irreversible structural damage.
How Smart Oral Care Supports Prevention
AI-guided toothbrush technologies like BrushO assist users in maintaining protective habits that reduce tooth loss risk.
Pressure Monitoring
Prevents gum trauma that contributes to recession and instability.
Zone Coverage Tracking
Ensures complete plaque removal across all surfaces.
Habit Reports
Identifies behavioral patterns linked to oral health decline.
Personalized Brushing Modes
Adapt intensity to protect sensitive or at-risk areas.
These tools support long-term preservation of dental and bone structure through consistent daily feedback.
When Tooth Loss Occurs
Dental professionals may recommend:
• Implants
• Bridges
• Dentures
These interventions restore function and partially preserve bone stimulation, though prevention remains the optimal strategy.
Tooth loss triggers structural changes that extend far beyond missing teeth. Reduced bone stimulation leads to jaw resorption, facial contour alteration, and functional complications. Recognizing this connection reinforces the importance of preventive oral hygiene and consistent monitoring. Combining daily care practices with intelligent brushing guidance — such as provided by BrushO — helps reduce the risk of periodontal decline and supports lifelong structural health. Oral health preservation is not only about maintaining a smile — it is about protecting the architecture of the face itself.
Popular
How to Build the Perfect Oral Care Routine in 2025
Jul 30
Why Your Gums Bleed and How to Fix It Fast in 2025
Jul 30
Top 5 Oral Care Mistakes and How BrushO Fixes Them
Jul 29
What Makes a Toothbrush “Smart”?
Jul 22
BrushO Smart Toothbrush: Gentle, Powerful, Travel-Friendly
Jul 19
BrushO: The Future of Smart Oral Care—Redefining the Way You Brush
Jul 17
Recent Posts
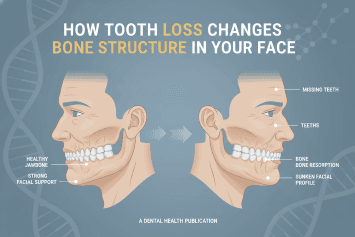
How Tooth Loss Changes Bone Structure in Your Face
Learn how tooth loss affects facial bone structure, jaw stability, and appearance. Discover prevention strategies and smart oral care tools to protect long-term oral health.
The Link Between Gum Loss and Facial Aging
Discover how gum recession contributes to facial aging, jaw structure changes, and smile aesthetics. Learn prevention strategies and smart oral care solutions.

How Antibiotics Permanently Change Your Mouth
Learn how antibiotics reshape your oral microbiome, affecting bacteria balance, gum health, and breath. Discover how to protect your mouth after antibiotic use.

Good vs Bad Mouth Bacteria
Discover the difference between good and bad mouth bacteria and how maintaining oral microbiome balance protects teeth, gums, and overall health through proper hygiene and smart brushing.
The Immune Cost of Chronic Gum Inflammation
Chronic gum inflammation weakens immune defenses and increases systemic disease risk. Learn how periodontal inflammation impacts immunity and how to protect oral health.
Why Frequent Mouth Infections Signal Immune Weakness
Frequent mouth infections may be a warning sign of immune system weakness. Learn how oral infections reveal hidden health risks and how to protect your immunity.

Can Mouth Bacteria Affect Mood and Anxiety?
Emerging research shows that oral bacteria can influence mood, anxiety, and emotional balance through inflammation and the gut–brain axis. Discover how oral health impacts mental health.
How Oral Inflammation Affects Brain Fog and Memory
Oral inflammation doesn’t just damage your gums — it can disrupt brain function, trigger brain fog, and weaken memory. Discover how gum disease and oral bacteria affect cognitive health and how to protect your mind through smarter oral care.

Should You Brush Before or After Taking Vitamins?
Should you brush before or after taking vitamins? Learn how supplements affect enamel, saliva, and bacteria — and how smart brushing with BrushO protects your teeth.
The Unexpected Link Between Oral Health and Skin Breakouts
Discover how poor oral health can trigger acne and skin breakouts through bacteria, inflammation, and immune stress — and how smart brushing can protect both your smile and your skin.
