Popular
How to Build the Perfect Oral Care Routine in 2025
Jul 30
Why Your Gums Bleed and How to Fix It Fast in 2025
Jul 30
Top 5 Oral Care Mistakes and How BrushO Fixes Them
Jul 29
What Makes a Toothbrush “Smart”?
Jul 22
BrushO Smart Toothbrush: Gentle, Powerful, Travel-Friendly
Jul 19
BrushO: The Future of Smart Oral Care—Redefining the Way You Brush
Jul 17
Back
How Antibiotics Permanently Change Your Mouth11h ago
11h ago
Antibiotics are life-saving medications that eliminate harmful bacteria throughout the body, but their effects extend far beyond treating infections. They also disrupt the oral microbiome — the complex ecosystem of microorganisms responsible for protecting teeth, gums, and immune balance. Changes in microbial composition can alter saliva chemistry, bacterial diversity, and susceptibility to oral disease long after treatment ends. Understanding how antibiotics reshape oral health helps individuals take preventive steps to restore balance, reduce long-term risks, and maintain resilient hygiene habits supported by smart oral care technologies.

Understanding How Antibiotics Affect the Mouth
Antibiotics work by destroying or inhibiting bacterial growth. However, they do not distinguish between harmful and beneficial bacteria.
When antibiotics circulate through the saliva and bloodstream, they affect:
• Oral microbial diversity
• Biofilm composition on teeth
• Saliva chemistry
• Immune signaling within gum tissue
These changes can influence oral health weeks or even months after treatment.
The Oral Microbiome Disruption
Loss of Beneficial Bacteria
Beneficial microbes regulate pH levels and compete against harmful pathogens. Antibiotics reduce these protective populations, allowing opportunistic bacteria or fungi to dominate.
Potential outcomes include:
• Increased plaque formation
• Higher cavity susceptibility
• Oral yeast overgrowth
• Gum sensitivity
Microbial ecosystems rarely return to identical pre-treatment states.
Altered Bacterial Balance
After antibiotic exposure, new microbial communities may form. These communities can behave differently, affecting:
• Breath odor production
• Acid generation
• Inflammatory response
• Plaque adhesion patterns
This shift explains why some individuals notice oral changes even after finishing medication.
Common Oral Side Effects
Dry Mouth
Antibiotics may influence saliva flow or gland response. Reduced saliva weakens natural cleansing mechanisms and increases bacterial accumulation.
Taste Changes
Microbial imbalance can temporarily alter taste perception or cause metallic flavors.
Increased Sensitivity
Enamel exposure and gum inflammation may occur if bacterial balance shifts toward acid-producing strains.
Higher Risk of Gum Irritation
Immune modulation during microbial repapping can trigger mild inflammatory responses.
Why Effects Can Be Long-Lasting
Microbiomes are adaptive systems. When antibiotics reshape the environment:
• Some species disappear
• Others permanently dominate
• New ecological balance forms
Research shows microbial composition may never fully revert, particularly after repeated antibiotic exposure. This does not necessarily mean damage, but it does mean habits must adapt.
Supporting Oral Recovery After Antibiotics
Reinforce Hygiene Consistency
Thorough plaque removal prevents opportunistic bacterial overgrowth during microbiome stabilization.
Maintain Hydration
Saliva helps restore ecological balance and neutralize acids.
Balanced Nutrition
Fiber-rich foods support microbial recovery and immune function.
Monitor Brushing Technique
Improper pressure or missed zones increase risk during microbiome vulnerability.
How Smart Brushing Technology Helps
AI-guided tools like BrushO assist users in maintaining stability during microbial transitions.
Coverage Monitoring
Ensures plaque removal across all zones while bacterial communities rebalance.
Pressure Feedback
Protects gum tissues that may be temporarily sensitive.
Habit Tracking
Encourages consistency when routine disruptions occur during illness.
Personalized Modes
Allows gentler cleaning for post-treatment sensitivity.
Technology does not replace recovery — but it supports optimal conditions.
Long-Term Oral Health Perspective
Antibiotics remain essential medical tools, yet awareness of their oral impact allows proactive care.
Maintaining bacterial equilibrium through:
• Structured hygiene routines
• Balanced microbial support
• Consistent monitoring
helps preserve resilience in oral ecosystems and prevents secondary complications.
Antibiotics reshape the oral microbiome in ways that can extend beyond treatment. While these medications protect systemic health, they also alter bacterial diversity, saliva dynamics, and oral balance. Understanding these changes empowers individuals to respond with intentional hygiene practices and supportive technologies. With intelligent guidance, habit tracking, and precision brushing, solutions like BrushO help users maintain stability and protect oral health through microbiome transitions. Oral health is not static — it evolves with every biological and lifestyle influence, and informed care ensures it evolves in the right direction.
Popular
How to Build the Perfect Oral Care Routine in 2025
Jul 30
Why Your Gums Bleed and How to Fix It Fast in 2025
Jul 30
Top 5 Oral Care Mistakes and How BrushO Fixes Them
Jul 29
What Makes a Toothbrush “Smart”?
Jul 22
BrushO Smart Toothbrush: Gentle, Powerful, Travel-Friendly
Jul 19
BrushO: The Future of Smart Oral Care—Redefining the Way You Brush
Jul 17
Recent Posts
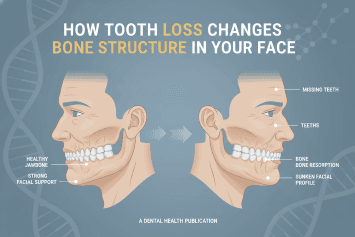
How Tooth Loss Changes Bone Structure in Your Face
Learn how tooth loss affects facial bone structure, jaw stability, and appearance. Discover prevention strategies and smart oral care tools to protect long-term oral health.
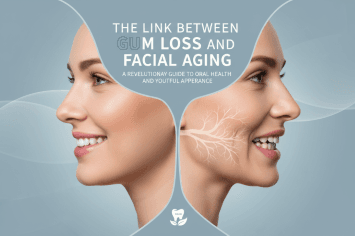
The Link Between Gum Loss and Facial Aging
Discover how gum recession contributes to facial aging, jaw structure changes, and smile aesthetics. Learn prevention strategies and smart oral care solutions.

How Antibiotics Permanently Change Your Mouth
Learn how antibiotics reshape your oral microbiome, affecting bacteria balance, gum health, and breath. Discover how to protect your mouth after antibiotic use.

Good vs Bad Mouth Bacteria
Discover the difference between good and bad mouth bacteria and how maintaining oral microbiome balance protects teeth, gums, and overall health through proper hygiene and smart brushing.
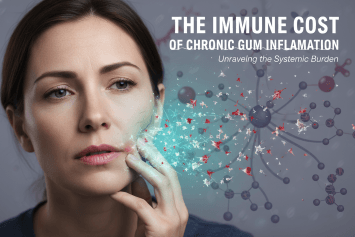
The Immune Cost of Chronic Gum Inflammation
Chronic gum inflammation weakens immune defenses and increases systemic disease risk. Learn how periodontal inflammation impacts immunity and how to protect oral health.
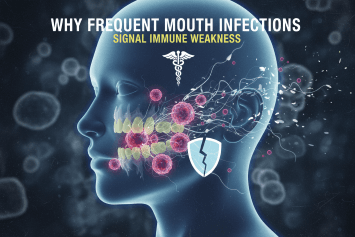
Why Frequent Mouth Infections Signal Immune Weakness
Frequent mouth infections may be a warning sign of immune system weakness. Learn how oral infections reveal hidden health risks and how to protect your immunity.

Can Mouth Bacteria Affect Mood and Anxiety?
Emerging research shows that oral bacteria can influence mood, anxiety, and emotional balance through inflammation and the gut–brain axis. Discover how oral health impacts mental health.
How Oral Inflammation Affects Brain Fog and Memory
Oral inflammation doesn’t just damage your gums — it can disrupt brain function, trigger brain fog, and weaken memory. Discover how gum disease and oral bacteria affect cognitive health and how to protect your mind through smarter oral care.

Should You Brush Before or After Taking Vitamins?
Should you brush before or after taking vitamins? Learn how supplements affect enamel, saliva, and bacteria — and how smart brushing with BrushO protects your teeth.
The Unexpected Link Between Oral Health and Skin Breakouts
Discover how poor oral health can trigger acne and skin breakouts through bacteria, inflammation, and immune stress — and how smart brushing can protect both your smile and your skin.
